Aspadol 200 mg vs. Tramadol: Which Is More Effective?
Compare Aspadol 200 mg (tapentadol) and tramadol for pain relief. Learn about mechanisms, efficacy, side effects, abuse potential, and expert guidance to choose the right medication.
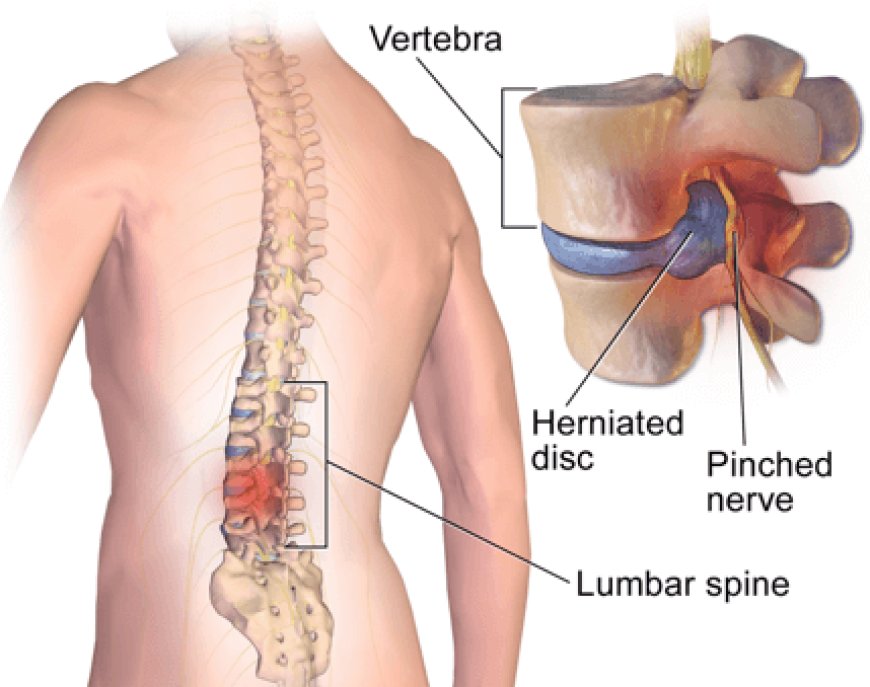
Selectingtheappropriateopioid analgesic isessentialinorderto treatpainsafelyandeffectively. Twoof the mostcommonly prescribedmedicationsare Aspadol 200?mg (tapentadol) and tramadol.Althoughtheysharesomedifferences, theyarevastlydifferentregardingmechanism of action,potency, side effect profiles, andaddictionliability.Belowisacomprehensivecomparison toaidyou and yourphysicianinmakingawell-informed decision.
1. Mechanism of Action: Dual vs Mixed
Tapentadol (Aspadol)
-
Dual-action: ?opioid receptor (MOR) agonist and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI) .
-
Providesanalgesiathroughboth opioid and monoaminergicmechanisms.
Tramadol
-
Mixedaction: weak MOR agonist and serotonin?norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).
-
Requires metabolic activation (by CYP2D6) to its active metabolite O?desmethyltramadol .
Takeaway: Tapentadols direct NRI action and full MOR activity mean more consistent pain control with fewer inter-patient differences.
2. Onset & Potency
-
Tapentadol (IR form) reaches peak blood levels in ~12 hours, lasting ~46 hours .
-
Compared to morphine potency, tapentadol is stronger than tramadol (potency between tramadol and morphine) .
-
Studies find tapentadol 100250?mg bid is 25 more potent than tramadol in animal models .
Summary: Tapentadol offers faster, more potent pain relief.
3. Efficacy in Clinical Pain Models
Chronic Pain & Neuropathic Pain
-
Tapentadol is effective in neuropathic and nociceptive painsuperior to many pure opioids .
-
Also effective for diabetic neuropathy and low back pain with neuropathic components .
Head-to-Head & Meta-Analysis
-
One network meta-analysis found tramadol 300?mg qd gave ~46% pain reduction vs baseline vs tapentadol's 36% (100250?mg bid) at 12 weeks .
-
The 0.7?point difference on a 010 pain scale was statistically significant, but not clinically meaningful .
4. Side Effects and Tolerability
Tapentadol
-
Causes less nausea and constipation versus tramadol and oxycodone .
-
Possible side effects: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, dry mouth .
Tramadol
-
Shares similar side effects but often induces more constipation, nausea, vomiting .
-
Tramadol also carries higher seizure risk and serotonin syndrome risk due to SNRI activity .
Conclusion: Both carry opioid risks, but tapentadol tends to be better tolerated.
5. Metabolism & Drug Interactions
Tapentadol
-
Undergoes glucuronidation, with no active CYP-derived metabolites .
-
Fewer interactions and no dependence on CYP polymorphisms.
Tramadol
-
Requires CYP2D6 metabolismefficacy and safety influenced by genetic variations .
-
Greater potential for drugdrug and interpatient variability.
6. Abuse, Dependence & Withdrawal
-
Tapentadol has lower abuse potential than stronger opioids, but still significantsimilar to hydrocodone .
-
Tramadol was once considered low-risk, but WHO data indicates rising abuse, especially via misuse .
Withdrawal Comparisons:
-
Tapentadol: typical opioid withdrawal symptoms.
-
Tramadol: includes opioid withdrawal plus SNRI discontinuation symptoms like anxiety, paresthesia .
7. Cost-Effectiveness
A Spanish study found tapentadol to be cost-effective vs morphine and tapentadol prolongs quality-adjusted life years at 2,656 per QALY gained .
Comparable tramadol cost/QALY data is lacking, but tapentadol's better tolerability may offset its higher cost.
8. Choosing the Right Option: Which One to Use?
| Criteria | Tapentadol (Aspadol) | Tramadol |
|---|---|---|
| Potency | Moderate?Severe pain | Mild?Moderate pain |
| Mechanism | MOR + NRI (dual) | MOR + SNRI (metabolite-dependent) |
| Neuropathic Pain | Effective | Limited evidence |
| Side Effects | Less GI burden | More constipation/nausea |
| Interaction Risk | Low (no CYP) | Higher (CYP2D6 involvement) |
| Abuse Potential | Moderate | Increasing misuse risk |
| Withdrawal Severity | Mild?Moderate | Opioid + SNRI symptoms |
| Genetic Variability | Minimal | Significant |
Summary & Recommendations
-
Efficacy: Both work, but tramadol may slightly reduce pain more in some chronic studiesthough this may not be clinically noticeable.
-
Side Effects & Safety: Tapentadol offers a fewer and milder adverse effects, especially gastrointestinal.
-
Drug Interactions: Tapentadol avoids CYP variability, making it a safer choice if you're on multiple meds.
-
Abuse/Dependence: Neither is benign. Tapentadol carries moderate risk; tramadol withdrawal may be more complex.
Bottom Line: For moderate to severe pain, especially neuropathic or when GI tolerability matters, tapentadol (Aspadol 200?mg) is often the superior choice. If you have mild pain and fewer comorbidities, tramadol remains viablebut use with caution.